Management of orbital roof fractures varies based on individual clinical features including the presence of exophthalmos gaze restriction and concomitant injuries such as dural tears.
Orbital roof fracture management.
Investigation of orbital fractures is by x ray and ct with ct being the modality of choice though it can be unreliable in children with blowout fractures.
A ct may already be appropriate due to a mechanism of injury or red flags for a head injury.
An interdisciplinary approach with plastic surgery ophthalmology and neurosurgery is crucial to providing comprehensive care.
Mazzoli highlighted this contingency in children because roof fractures are much more common for them than for adults.
Another potential emergency involves the roof not the floor of the orbit.
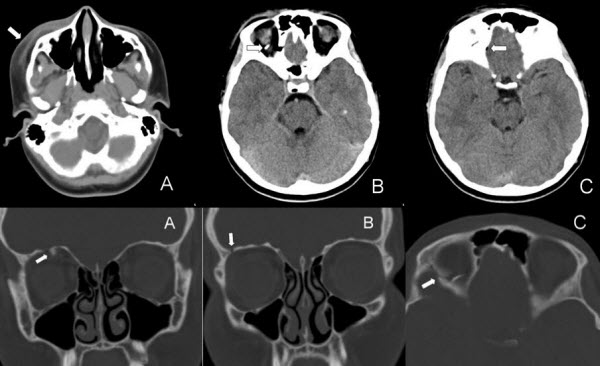
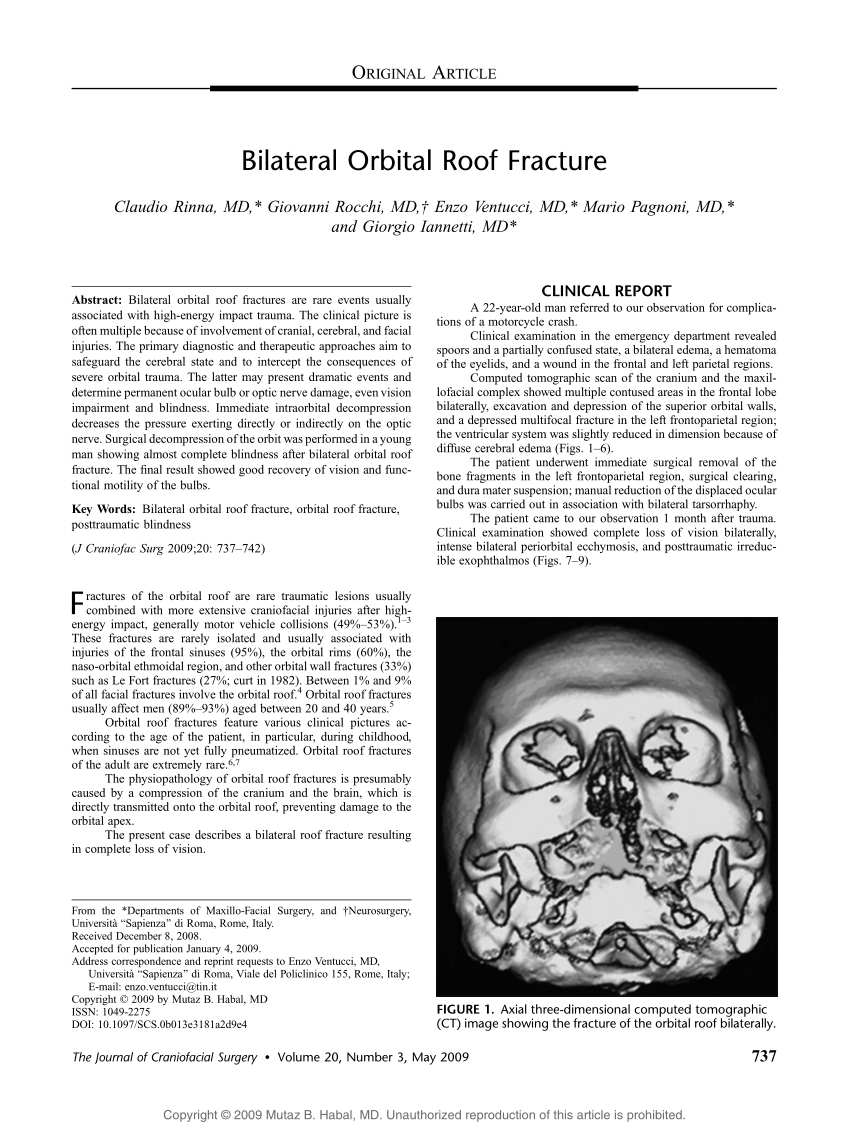
Traumatic orbital roof fractures are rare and are managed nonoperatively in most cases.
That s because they go headfirst over handlebars and tend to do a forehead plant.
Approaches include extracranial intracranial and endonasal endoscopic.
Even in the context of floor fractures dr.
However intracranial or intraorbital injury may warrant surgical intervention to remove impinging bony fragments repair dura or reconstruct the orbital roof.
After a thorough ophthalmic exam and after other trauma has been ruled out the patient and physician.
Most can be safely observed.
Nondisplaced or minimally displaced orbital roof fractures are usually managed by observation but displaced orbital roof fractures can cause ophthalmic and neurologic complications and open surgical intervention is occasionally required.
In cases of minor isolated orbital roof fractures where no surgical intervention is needed the patient.